Type 2 Diabetes Health Conditions
Are you suffering from Type 2 Diabetes? Type 2 Diabetes is affected for all ages and dangerius to your health. So get the symptoms, prevention details, risk factors, managing diabetes, insulin details, diagnosing diabetes, damage conditions and tips to prevent type 2 diabetes are given below. View the full details of type 2 diabetes and care your health which was given below
Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes strikes people of all ages, and early symptoms are subtle. In fact, about one out of three people with type 2 diabetes don't know they have it. Diabetes is a chronic condition that thwarts the body's ability to change food into energy. This allows sugar levels to build up in the blood, which can increase the risk of heart disease, loss of vision, and other serious complications.What are the Symptoms of Type 2 Diabetes?
1) Thirst :
One of the first symptoms of type 2 diabetes may be an increase in thirst. This is often accompanied by additional problems, including dry mouth, increased appetite, frequent urination — sometimes as often as every hour — and unusual weight loss or gain.
2) Headaches :
As blood sugar levels become more abnormal, additional symptoms may include headaches, blurred vision, and fatigue.
3) Infections :
In most cases, type 2 diabetes is not discovered until it takes a noticeable toll on health. One red flag is troubling infections, such as:
* Cuts or sores that are slow to heal
* Frequent yeast infections or urinary tract infections.
* Itchy skin, especially in the groin areaWhat are the Risk Factors of Type 2 Diabetes?
1) Risk Factors You Can Control :
* Being overweight, defined as a body mass index (BMI) over 25
* Sedentary lifestyle
* Abnormal cholesterol and blood fats, such as HDL "good" cholesterol lower than 35 mg/dL or a triglyceride level over 250 mg/dL
* High blood pressure greater than 140 /90 in adults
* Smoking
2) Risk Factors You Can't Control :
* Race or ethnicity: Hispanics, African Americans, Native Americans, and Asians have a higher than average risk.
* Family history of diabetes: Having a parent or sibling with diabetes boosts your risk.
* Age: Being 45 and older increases your risk of type 2 diabetes.
The more risk factors you have, the greater your odds of developing type 2 diabetes.
3) Risk Factors for Women :
Having gestational diabetes when you're pregnant puts you at higher risk for developing type 2 diabetes later on. Women who give birth to a baby weighing over 9 pounds are also at risk. Having a history of polycystic ovary syndrome can also cause insulin resistance that can lead to diabetes.How to Diagnose Type 2 Diabetes ?
1) A simple blood test can diagnose diabetes:
* The A1C test gives a snapshot of your blood glucose level over the past two to three months.
* An A1C level of 6.5% or more is consistent with the diagnosis of diabetes. A fasting plasma glucose test is another option.
* You must not eat for eight hours before the test.
* A result above 126 is considered diabetes.
* An oral glucose challenge test with a two-hour blood test may also help your doctor make a diagnosis.
How to Manage Type 2 Diabetes?
1) Diet :
Fortunately, controlling blood sugar levels by changing diet can also cut your risk of complications. People with type 2 diabetes should carefully monitor carbohydrate consumption, as well as total fat and protein intake, and reduce calories. Ask your doctor for a referral to a registered dietitian to help you with healthy choices and an eating plan that will work for you.
2) Exercise :
Moderate exercise, such as strength training or walking, improves the body's use of insulin and can lower blood sugar levels in people with type 2 diabetes. Being active also helps reduce body fat, lower blood pressure, and protect against heart disease. People with type 2 diabetes should try to get 30 minutes of moderate exercise on most days of the week.
3) Stress Reduction :
Stress can cause blood pressure to rise. Or you may turn to food to cope. Both are bad when living with diabetes. Instead of letting stress take its toll, try practicing relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, or visualization. Sometimes talking to a friend, family member, counselor, or member of the clergy can help. If you're still battling stress, reach out to your doctor.
4) Oral Medication :
When people with type 2 diabetes are unable to control blood sugar sufficiently with diet and exercise, medication may be added. There are many types of diabetes pills available, and they are often used in combination. Some work by stimulating the pancreas to make more insulin, and others improve the effectiveness of insulin, or block the digestion of starches.
5) Insulin :
Your doctor may prescribe insulin early in on your treatment and in combination with pills. Insulin is also used in people with type 2 diabetes who develop "beta-cell failure." This means the cells in the pancreas no longer produce insulin in response to high blood sugar levels. In this case, insulin therapy — injections or an insulin pump — must become part of the daily routine.
What are the Long-Term Damage for Type 2 Diabetes?
1) Long Term effect of Diabetes 2 on Arteries :
Over time, untreated type 2 diabetes can damage many of the body's systems. About two out of three people with diabetes die of heart disease. Having diabetes also puts you at a two to four times higher risk for stroke. People with diabetes are likely to develop plaque in their arteries, reducing blood flow and increasing risk of clots. This hardening of the arteries (atherosclerosis) raises the risk of heart attack and stroke.
2) Long Term effect of Diabetes 2 on Kidneys :
The longer you have diabetes, the greater the risk of developing chronic kidney disease. Controlling risk factors such as uncontrolled diabetes, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol reduces your risk of developing this complication. Annual screening for kidney disease and medications, which slow the development and progression of kidney disease, are used to reduce your risk of kidney failure.
3) Long Term effect of Diabetes 2 on Eyes :
High blood sugar can damage the tiny blood vessels that bring oxygen and nutrients to the retina, a critical part of the eye. This is known as diabetic retinopathy, and it can cause progressive, irreversible vision loss. It is the leading cause of blindness in people between the ages of 20 and 60. Pools of blood, or hemorrhages, on the retina of an eye are visible in this image.
4) Long Term effect of Diabetes 2 on Nerves :
Uncontrolled diabetes, and elevated blood sugars over time, increases the risk of nerve damage. Symptoms include tingling, numbness, pain, and a pins and needles feeling in the fingers, hands, toes and feet . Nerve damage (neuropathy) can't be reversed but treatments may help pain and numbness. Nerve damage can also affect other parts of your body such as your digestive system. Controlling your diabetes can help prevent further damage.How to Prevent Type 2 Diabetes disease?
One of the most astonishing things about type 2 diabetes is that such a life-altering condition is often preventable. To lower your risk, follow the same guidelines for warding off heart disease:
* Eat a healthy diet
* Exercise for 30 minutes, five days a week
* Maintain a healthy weight
* Talk to your doctor about being screened for prediabetes
* In people with prediabetes, lifestyle changes and medication can help prevent the progression to type 2 diabetes.
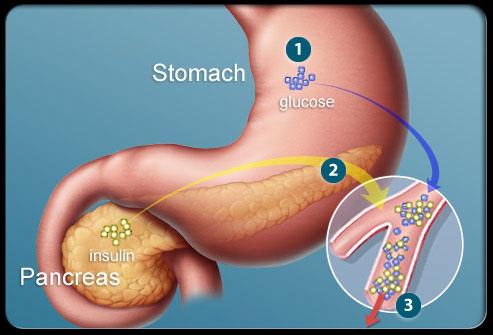
Insulin: Turning Glucose Into Energy
1) After eating, the stomach breaks carbohydrates down into sugars, including glucose.
2) Glucose enters the bloodstream and stimulates the release of insulin from the pancreas.
3) Insulin and glucose travel in the blood to all the body's cells. Insulin allows glucose to enter the cells and be used as fuel. Excess glucose is stored in the liver.
In diabetes, the cells cannot absorb glucose properly. That means glucose levels in the blood become elevated. With insulin resistance, the body makes excess insulin but the muscle, liver, and fat cells do not use or respond properly to insulin. With long-standing, uncontrolled type 2 diabetes the pancreas will reduce the amount of insulin it produces.
