Sinusitis: Classifications, symptoms and treatment.
Sinusitis is an inflammation of the air filled cavities within the nostrils and the nasal passage of the nose. It can be caused by pathogenic micro organism (virus, bacteria or fungus) and also by allergies and chemical fume.
Sinuses (Para nasal sinuses) are air filled spaces are found in the skull which help in protecting skull from heat, cold or noise, reduce the weight, and allow the sound to resonate within the skull. Inflammation of these sinuses can be caused by pathogenic micro-organisms (virus, bacterium or fungus) and also by allergies and chemicals.
Human skull contains four major pairs of air filled cavities known as sinuses.
These sinuses are connected to the space between nostrils and the nasal passage. Main pairs of sinuses are as follows: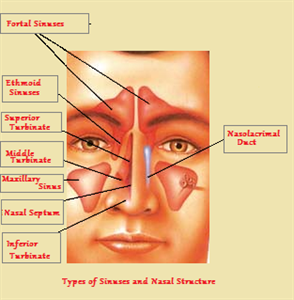
Frontal sinuses:
Frontal sinuses are found in the forehead.Maxillary sinuses:
Maxillary sinuses are found behind the cheek bone.Ethmoid sinuses:
Ethmoid sinuses are found between the two eyes.Sphenoid sinuses:
Sphenoid sinuses are found behind the eyes.Risk factors of sinusitis :
In case of adults and children risk factors for sinusitis are as follows:
•Common cold/ influenza
•Allergic rhinitis
•Nasal septum deviation
•Smoking
•Nasal polyp
•Diseases that prevent small hairs (cilia)from working properly
•Nasal bone spur
•Cystic fibrosis
•Day care in case of children
•Changes in altitude
•Weak immune system in case of chemotherapy or HIV.Types of sinusitis :
Sinusitis can be categorised in number of ways based on:
1. Duration or Span of time taken (acute, sub acute or chronic sinusitis)
2. Type of inflammation i.e. infectious sinusitis or non infectious sinusitis and
3. Location of sinusitis (frontal, maxillary, ethmoid and sphenoid sinusitis)Sinusitis based on duration (Span of time taken) :
Sinusitis can be:Acute sinusitis:
Acute sinusitis lasts for less than 4 weeks duration. It is usually triggered by a previous upper respiratory tract infection, mostly viral origin. It is less often caused by bacteria, of which Haemophilus influenzae, Streptococcus pneumonae, and Moraxella catarrhalis, are most common causative once. Viral sinusitis typically lasts for 7 to 10 days while bacterial sinusitis is more persistent. Roughly 2% of viral sinusitis can be converted into bacterial sinusitis by secondary bacterial infection.
Acute sinusitis may occur from fungal invasion especially in patients with diabetes and AIDS.
Chemical irritants may triggers acute sinusitis, by cigarette smoke and chlorine fumes. Rarely tooth infection can cause sinusitis.Sub acute sinusitis:
Sub-acute sinusitis lasts more than 4 weeks to 12 weeks.Chronic sinusitis:
Chronic sinusitis lasts more than 12 weeks and continues for several months or even years and can be caused by several diseases that have chronic inflammation of the sinuses. Symptoms of chronic sinusitis are: headache, nasal congestion, night-time coughing, facial pain, an increase in asthma symptoms, malaise, thick green/ yellow discharge, feeling of tightness or fullness that may increase on bending, aching teeth, dizziness. Often chronic sinusitis can lead to decreased sense of smell. In very few cases, acute or chronic maxillary sinusitis is associated with dental infection.
All the three types of sinusitis have more or less had similar symptoms and are often difficult to differentiate. Acute sinusitis is most common amongst them. In majority of cases adults have sinusitis in their life. Sinusitis based on the type of inflammation :
Infectious sinusitis :
Often caused by virus and less frequently by bacteria and fungus, Sub acute and chronic sinusitis occurs as a result of incomplete treatment of an acute sinusitis.Non-infectious sinusitis :
Non-infectious sinusitis is mostly caused by allergic conditions & irritants.Sinusitis based on location of sinusitis :
There are several number of sinuses (paranasal sinuses), such as frontal, maxillary, ethmoid and sphenoid sinuses. In addition to the severity of the disease mentioned above, sinusitis can be classified by the sinus air space which it affects:
1. Frontal sinusitis can cause pain or tenderness in the frontal sinus cavity (situated above the eyes), and headache.
2. Maxillary sinusitis cause pain or tenderness in the cheek area viz. toothache and headache.
3. Ethmoid sinusitis can cause pain or tenderness between or behind the eyes and headache.
4. Sphenoid sinusitis can cause pain or tenderness behind the eyes. Pain of sphenoid sinusitis usually refers to the top of the head.
All forms of sinusitis may either result in, or be a part of, an inflammation of the airway, so other airway symptoms, such as cough, may be associated with it. Signs and symptoms of sinusitis :
All the forms of sinusitis have more or less same symptoms. Most common symptoms of sinusitis are:
1. Headache with facial tenderness, pressure or pain in the sinus.
2. Fever
3. Cloudy, discoloured nasal discharge
4. Sore throat
5. Feeling of nasal stuffiness
6. Cough (especially night-time coughing)
7. Bad breath or loss of smell
8. Malaise
9. Feeling of tightness or fullness that may increase on bending
10. Aching teeth
11. Dizziness: sinus infections can also cause ear problems due to nasal congestion leads to dizziness.
12. Itching eyes (allergic conjunctivitis)
13. Sneezing
14. Feeling of fatigue or weakness
15. Bacterial sinusitis is suspected when there is facial pain with pus like nasal discharge and symptoms persists more than a week and not responding to nasal medications.
16. Sinusitis is usually diagnosed on the basis of history and physical examination.
17. Early treatment of allergic sinusitis can prevent secondary bacterial infection.
18. Symptoms of chronic sinusitis are same as that of acute sinusitis but are milder lasts longer than 12 weeks.Complications of sinusitis:
Complications of sinusitis are very rare and they are:
1. Abscess
2. Meningitis
3. Osteomyelitis
4. Orbital cellulites (skin infection around the eye)
Diagnosis of sinusitis :
It is not an easy task to distinguish acute viral or bacterial sinusitis. If symptoms last less than 10 days, it is generally considered to be a viral sinusitis. When symptoms last more than 10 days, it is considered to be bacterial sinusitis. CT scan can confirm the acute sinusitis.
In case of chronic sinusitis only CT scan is not enough for diagnosing sinusitis. CT scan, nasal endoscopy and clinical symptoms all together are essential to make the diagnosis.
The health care provider will examine to exclude sinusitis by-
1. Examining the nose for signs of polyp
2. Trasillumination test: by shining a beam of light against the sinus to see signs of inflammation.
3. Tapping over the sinus area to find infection.
4. Viewing the sinuses through nasal endoscopy to diagnose sinusitis.
Labs tests that rule out the possible causes of chronic sinusitis include are:
1. Blood tests for HIV or other tests for poor immune system
2. Allergy test
3. Nasal cystoscopy
4. Cilia function test
5. Sweat chloride tests for cystic fibrosisTreatment of sinusitis :
Conservative or self-care treatment of sinusitis
1. Apply moist, warm washcloth on the face several times in a day.
2. Drink plenty of fluids in a day to thin the mucus.
3. Steam inhalation 2-4 times in a day.
4. Nasal irrigation may relief symptoms in chronic sinusitis.
5. Decongestant nasal spray can cause relief in symptoms but not used for longer time (more than 5 days).
6. To control sinus pain avoid flying when you have congestion. Also avoid temperature extremes, sudden change in temperature and bending forward with head down.
7. Try ibuprofen or acetaminophen in sinus pain & pressure.Medical treatment for Sinusitis
Majority of acute sinusitis cases are caused by viral infection which resolve without antibiotics within 10 days. If symptoms do not resolve within 10 days, antibiotics may be prescribed soon in following conditions:
1. Children having thick nasal discharge with cough which is not relieved after 2-3 weeks
2. Fever higher than 102 degree F
3. Pain in the face or headache
4. Severe swelling around the eyesCommon antibiotics used in sinusitis
1. Amoxicillin
2. Amoxicillin with Clavulanate
3. Fluoroquinolones
4. Clarithromycin and tetracycline like doxycycline when patient is allergic to pencillins.
5. Acute sinusitis can be treated for 10 days while chronic for 3-4 weeks.
6. Chronic sinusitis may need special medicines to treat fungal infections.
7. Nasal corticosteroid sprays and antihistaminic drugs may be used to decrease the swelling in case of nasal polyps or allergies.
Surgery: Surgical treatment is given to clean and drain the sinuses especially in those who fails to respond medical treatment after 3 months, or in patients who have more than 2 or 3 episodes of acute sinusitis in a year.
Fungal sinusitis requires surgery. Surgical repair of a deviated nasal septum or nasal polyps is required.Prevention of sinusitis:
1. Best way to prevent sinusitis is to avoid or quickly treat common cold or influenza.
2. Eat fruits and green vegetables, which are rich in antioxidants and vitamins that can boost immune system and body resistance.
3. Avoid risk factors of sinusitis mentioned above.Prognosis of sinusitis:
Usually prognosis of disease is good. Sinusitis is usually curable disease with self- care and medical treatment. Recurrent attacks of sinusitis can be checked for underlying causes like nasal polyps or allergies.Other Names of Sinusitis:
There are 4 other names for Sinusitis. They are:
Acute sinusitis, Chronic sinusitis, Sinus infection, Rhinosinusitis
